Abstract
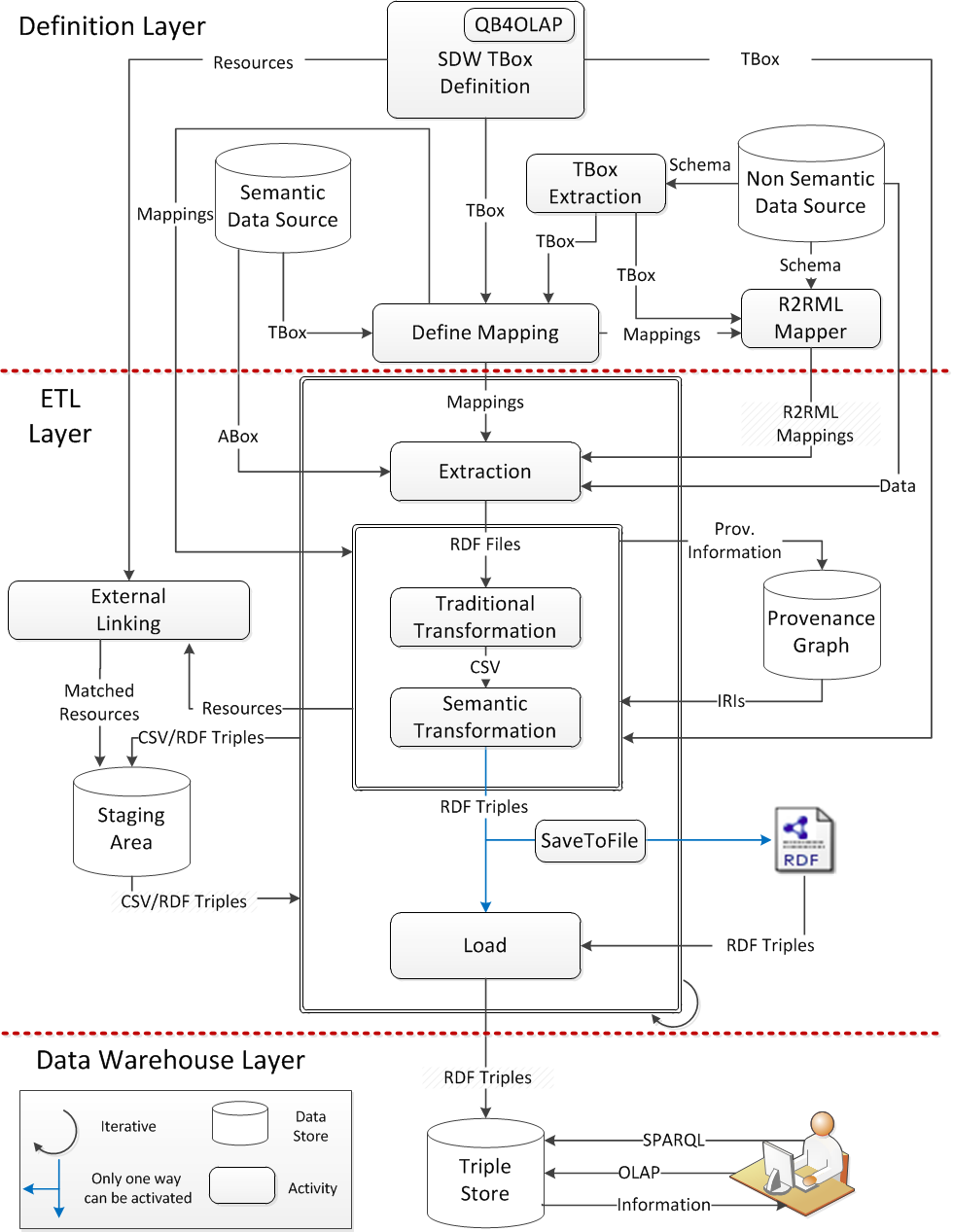
In order to create better decisions for business analytics, organizations increasingly use external structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in addition to the (mostly structured) internal data. Current Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) tools are not suitable for this “open world scenario” because they do not consider semantic issues in the integration processing. Current ETL tools neither support processing semantic data nor create a semantic Data Warehouse (DW), a repository of semantically integrated data. This paper describes our programmable Semantic ETL (SETL) framework. SETL builds on Semantic Web (SW) standards and tools and supports developers by offering a number of powerful modules, classes, and methods for (dimensional and semantic) DW constructs and tasks. Thus it supports semantic data sources in addition to traditional data sources, semantic integration, and creating or publishing a semantic (multidimensional) DW in terms of a knowledge base. A comprehensive experimental evaluation comparing SETL to a solution made with traditional tools (requiring much more hand-coding) on a concrete use case, shows that SETL provides better programmer productivity, knowledge base quality, and performance.
Authors: Rudra Pratap Deb Nath, Katja Hose, Torben Bach Pedersen, and Oscar Romero