Abstract
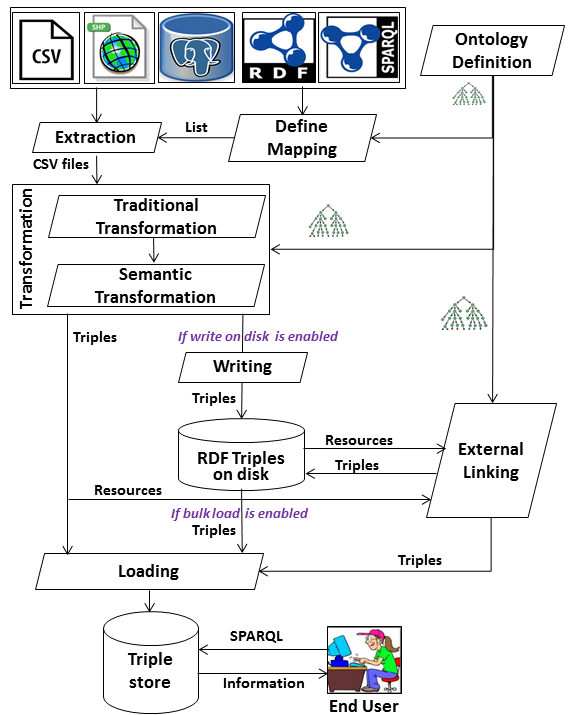
In order to create better decisions for business analytics, organizations increasingly use external data, structured, semistructured and unstructured, in addition to the (mostly structured) internal data. Current Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) tools are not suitable for this “open world scenario” because they do not consider semantic issues in the integration process. Also, current ETL tools neither support processing semantic-aware data nor create a Semantic Data Warehouse (DW) as a semantic repository of semantically integrated data. This paper describes SETL: a (Pythonbased) programmable Semantic ETL framework. SETL builds on Semantic Web (SW) standards and tools and supports developers by offering a number of powerful modules, classes and methods for (dimensional and semantic) DW constructs and tasks. Thus it supports semantic-aware data sources, semantic integration, and creating a semantic DW, composed of an ontology and its instances. A comprehensive experimental evaluation comparing SETL to a solution made with traditional tools (requiring much more handcoding) on a concrete use case, shows that SETL provides better performance, knowledge base quality and porgrammer productivity.
Authors: Rudra Pratap Deb Nath, Katja Hose, and Torben Bach Pedersen